Antimicrobial Resistance
- Home
- Antimicrobial Resistance
Antimicrobial
AMR knows no boundaries –
it can affect anyone, of any age, in any country.
AMR is the ability of a microorganism such as bacteria, viruses and parasites to stop an antimicrobial (e.g. antibiotics) from working against it.
AMR can also lead to treatments becoming ineffective and accelerate the spread of infections.
Microorganisms are increasingly harder to treat with antimicrobial medication.
More and more bacteria are becoming resistant to antibiotics.
Antivirals must constantly keep up with new mutations as well.
Resistance to antimalarials is also a growing problem.
No. of deaths attributable to AMR by 2050
10 million deaths per year are projected between 2015 and 2050 if current infection and resistance trends are not reversed. Only 0.7 million of these additional deaths would occur in North America or Europe, with the largest numbers in Africa and Asia.
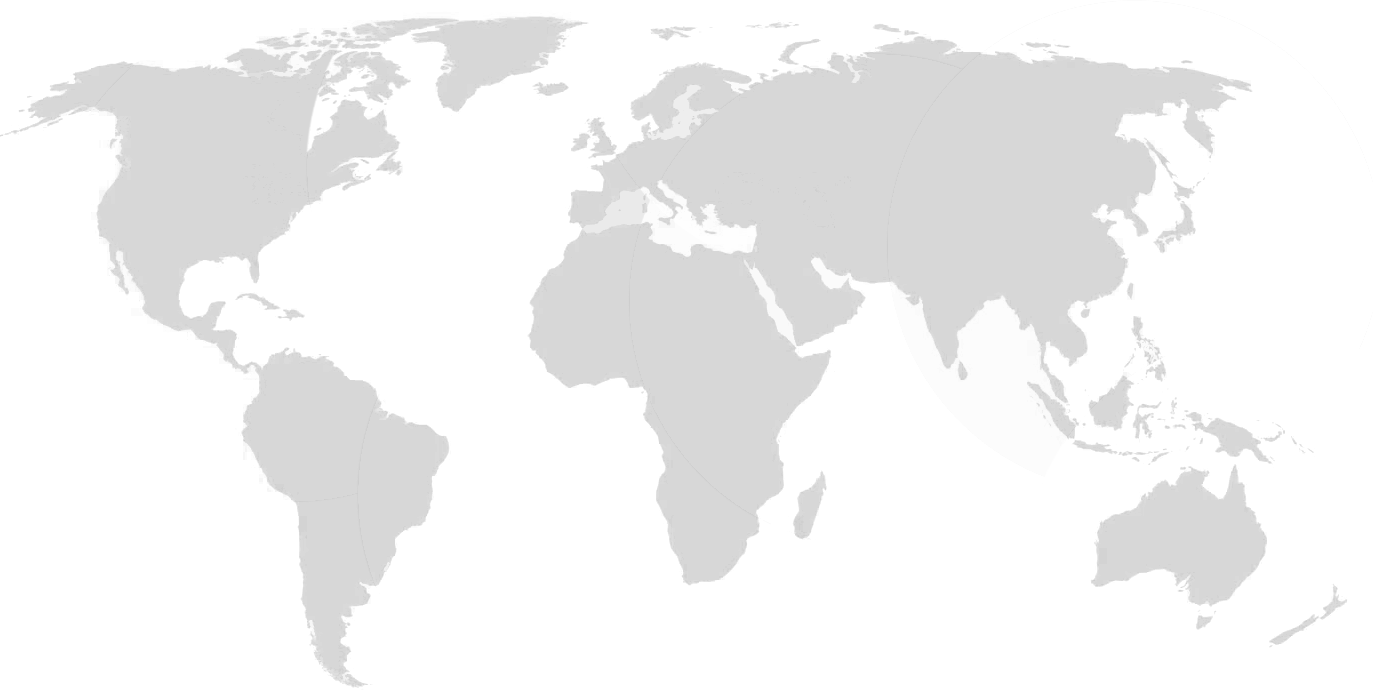
North America
317k
Latin America
392k
Europe
392k
Africa
4.1m
Asia
4.7m
Oceania
22k
Consequences of AMR
Globally, 700,000 deaths per year are already attributed to AMR
It is estimated that AMR has an impact of 1.5 billion EUR each year, making up extra healthcare costs and productivity losses due to multi-drug-resistant bacteria in the EU
Globally, it is estimated that only half of antibiotics are used correctly
Every three seconds, a death would be related to AMR by 2050
Infections and antibiotic consumption
Discover the fighter in you
Keep in mind
Overuse of antibiotics can cause bacteria to become resistant, meaning current treatments will no longer work.

Antibiotics are not always the answer. Do not demand antibiotics if your healthcare professional says you don’t need them.

Not all infections can be treated with antibiotics; antibiotics don’t cure viral infections such as cold and flu.

Only take antibiotics prescribed to you, do not share them with family or friends.

Above all, always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional when taking antibiotics.
Get more in-depth insights
from our expert interviews

Dr. Carl Shiu
«Sysmex feels AMR is a long-term concern that will impact all of us if we act too late and believe momentum for change will happen when information and education is widespread. Thus, we hope Sysmex’s proactive #AMRFighter efforts to raise awareness can lead to a future harmonized effort to adopt globally effective solutions for antibiotic stewardship and AMR reduction.»

Prof. Hsu Li Yang
«For human health and healthcare in the hospital settings, it is important that we continue to educate clinicians and other healthcare professionals and improve stewardship for better use of antibiotics.»
Prof. Dr. Shingo Yamamoto
«By improving what already exists on the market and through innovations that make it possible to detect antibiotic susceptibility in a short amount of time at the GP level, Prof Yamamoto is confident we will be able make a significant difference in patient management and fighting AMR.»

Dr. med. Peter Keller
«We need experienced diagnostic companies with experienced laboratory background to develop such [faster] tests. It’s a very interesting and important field of development.»

Dr. Ma Wai-Kit
«It is very worrisome to see the emergence of these resistant bacteria. […] As the use of antibiotics is partly driven by commercial reasons, despite the scientific support behind AMR, this battle is very challenging.»
Think you know what AMR is now?
Test your knowledge here!



Useful Links
© Copyright Sysmex Asia Pacific Pte Ltd - 2024 | All rights reserved.
